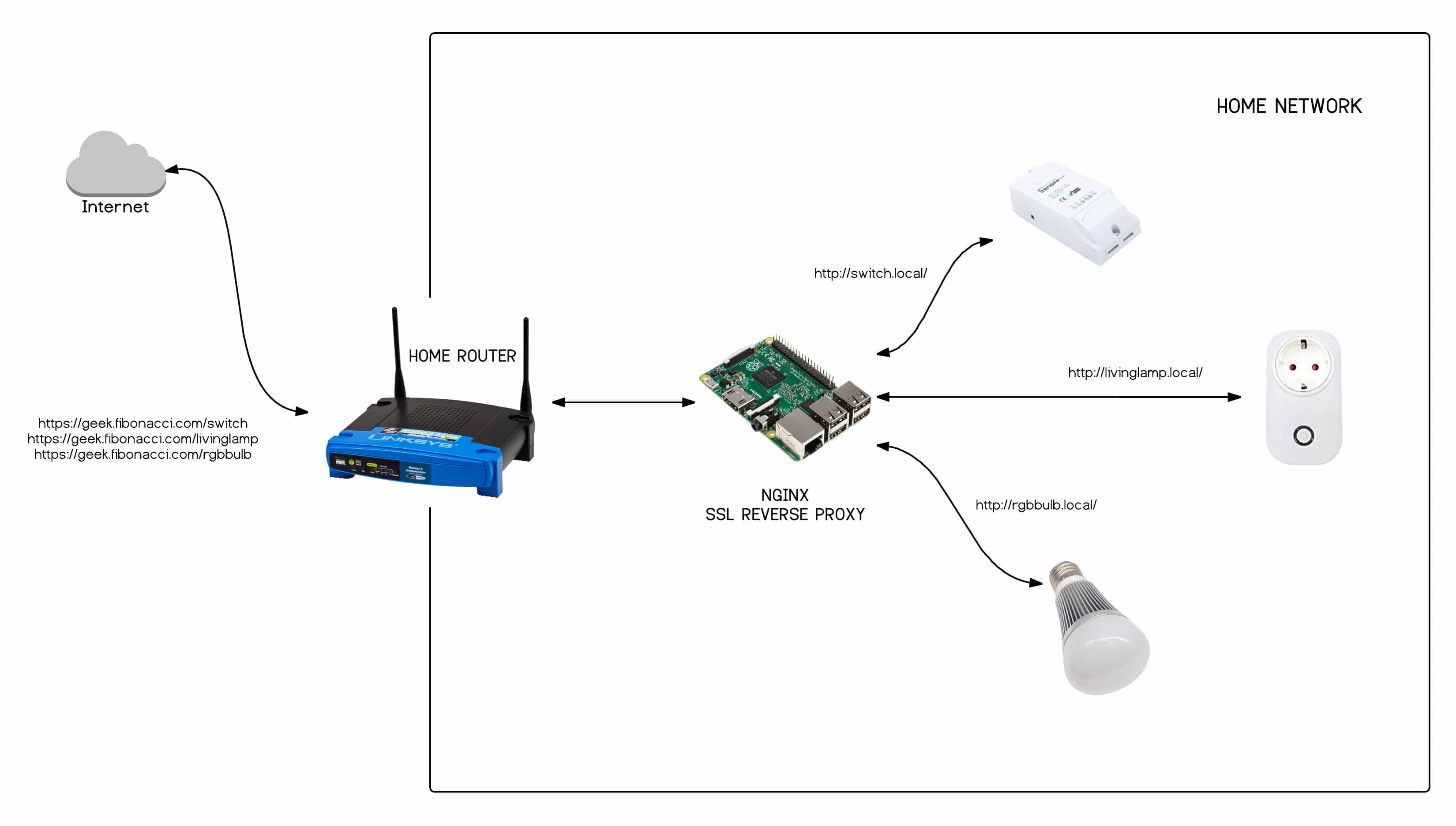
In today's interconnected world, managing IoT devices remotely has become essential for businesses and individuals alike. Remote SSH IoT Behind Example is a powerful technique that allows you to securely access and manage your IoT devices from anywhere in the world. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about setting up and using remote SSH for IoT devices, including practical examples and best practices. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or just starting with IoT technology, this article will provide you with valuable insights and actionable steps to enhance your device management capabilities.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how we interact with technology, connecting billions of devices worldwide. However, with this increased connectivity comes the challenge of managing these devices efficiently and securely. Remote SSH provides a reliable solution for accessing IoT devices behind firewalls and NAT networks, enabling administrators to maintain control without compromising security. This article explores the technical aspects of remote SSH while emphasizing its importance in modern IoT infrastructure.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll discover how remote SSH works in IoT environments, learn about its benefits and limitations, and gain practical knowledge through real-world examples. We'll also discuss essential security considerations and provide step-by-step instructions for implementing remote SSH in your IoT network. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you'll have a thorough understanding of how to leverage remote SSH for effective IoT device management.
Read also:Michelle Mulitz A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Understanding Remote SSH in IoT Environments
- Benefits and Limitations of Remote SSH
- Step-by-Step Setup Process
- Security Best Practices
- Real-World Examples
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Advanced Techniques and Tools
- Future Trends in Remote IoT Management
- Compliance and Regulatory Standards
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding Remote SSH in IoT Environments
Remote SSH (Secure Shell) serves as a fundamental protocol for secure communication between devices in IoT networks. Unlike traditional SSH connections, remote SSH in IoT environments often faces unique challenges due to devices being located behind firewalls, NAT networks, or in remote locations. The protocol establishes an encrypted tunnel that allows administrators to execute commands, transfer files, and manage configurations securely.
When dealing with IoT devices behind network barriers, several key concepts come into play:
- Port Forwarding: Essential for establishing connections through firewalls
- Reverse SSH Tunnels: Enables access to devices behind NAT
- Jump Hosts: Intermediate servers for secure connections
- Dynamic DNS: Maintains consistent access to devices with changing IP addresses
The technical architecture of remote SSH in IoT typically involves multiple layers of security protocols. According to recent industry statistics, over 60% of IoT device breaches occur due to weak or default credentials. This highlights the importance of implementing robust authentication mechanisms in remote SSH configurations.
Benefits and Limitations of Remote SSH
Implementing remote SSH for IoT management offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced security through end-to-end encryption
- Real-time device monitoring and control
- Reduced need for physical access to devices
- Improved operational efficiency
- Cost savings on maintenance and support
However, there are certain limitations to consider:
- Network latency can affect performance
- Requires proper configuration and maintenance
- Potential compatibility issues with legacy devices
- Increased complexity in network architecture
Step-by-Step Setup Process
Setting up remote SSH for IoT devices involves several critical steps:
Read also:Neil Tennant A Comprehensive Look At The Life And Career Of The Pet Shop Boys Icon
- Device Preparation: Ensure all devices have SSH services installed and configured properly.
- Network Configuration: Set up necessary port forwarding and firewall rules.
- Authentication Setup: Implement key-based authentication for enhanced security.
- Testing Connectivity: Verify connections from different network locations.
- Monitoring Implementation: Establish logging and monitoring mechanisms.
Authentication Methods
When implementing remote SSH, consider these authentication options:
- Password-based authentication (least secure)
- Public key authentication (recommended)
- Two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Certificate-based authentication
Encryption Protocols
Choose from these encryption standards:
- AES-256
- ChaCha20
- Blowfish
- 3DES (legacy systems)
Real-World Examples
Let's examine a practical implementation scenario:
A manufacturing company with 500 IoT sensors distributed across multiple factory locations implemented remote SSH management. By establishing reverse SSH tunnels through a central management server, they achieved:
- 95% reduction in on-site maintenance visits
- 70% faster issue resolution times
- Enhanced security compliance
- Centralized monitoring capabilities
Another example involves a smart agriculture project where remote SSH enabled farmers to monitor soil sensors and irrigation systems from their mobile devices, resulting in a 30% increase in crop yield efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When working with remote SSH IoT setups, you might encounter these common problems:
- Connection timeouts due to network issues
- Authentication failures
- Firewall blocking necessary ports
- Device resource limitations
Solutions include:
- Implementing keep-alive mechanisms
- Verifying SSH key permissions
- Configuring proper firewall rules
- Optimizing SSH configuration for low-resource devices
Advanced Techniques and Tools
For more complex IoT environments, consider these advanced approaches:
- Automated SSH tunnel management
- Containerized SSH services
- Zero-trust network architecture
- AI-powered anomaly detection
Future Trends in Remote IoT Management
The field of remote IoT management continues to evolve with these emerging trends:
- Edge computing integration
- Quantum-resistant encryption methods
- AI-driven security protocols
- Blockchain-based authentication
Compliance and Regulatory Standards
When implementing remote SSH for IoT, ensure compliance with these standards:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- ISO 27001 Information Security Management
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, remote SSH for IoT devices behind network barriers provides a secure and efficient method for device management. Throughout this guide, we've explored the technical foundations, implementation steps, security considerations, and real-world applications of remote SSH in IoT environments. The examples and best practices discussed demonstrate how organizations can leverage this technology to enhance their IoT infrastructure management while maintaining robust security protocols.
As you move forward with implementing remote SSH solutions, consider the following next steps:
- Conduct a thorough security audit of your current IoT setup
- Develop a comprehensive remote management strategy
- Implement regular security updates and patches
- Invest in staff training for secure SSH practices
We encourage you to share your experiences with remote SSH implementation in the comments below. If you found this guide helpful, please share it with your network and explore our other articles on IoT security and management. For any specific questions or technical challenges, our team of experts is available to provide guidance and support.